The benefits of hot and cold therapy have been recognized for centuries, offering a powerful, natural approach to managing pain, reducing inflammation, and accelerating recovery.
Think about that nagging ache in your lower back after a long day, the stiffness in your joints that makes movement a chore, or the lingering soreness that slows down your training progress.

We often reach for painkillers or resign ourselves to days of rest, but these solutions only mask the problem or temporarily halt our active lives. Relying solely on medication or inactivity can have limitations.
Painkillers only address the symptoms without addressing the underlying inflammation, while prolonged rest can lead to muscle weakness and stiffness.
What if you could tap into your body’s natural healing power to combat inflammation and recover faster?
Hot and cold therapy offers a safe, effective, and accessible solution to reduce pain, enhance recovery, and get you back to doing the things you love.
This comprehensive guide will explore the science behind hot and cold therapy, its remarkable benefits, and how you can harness its power to unleash your body’s innate ability to heal and thrive.
Hot & Cold Therapy Explained – The Science of Temperature & Healing
What is Hot and Cold Therapy?
Hot and cold therapy involves the application of temperature variations to the body to promote healing, reduce pain and inflammation, and enhance recovery.
This ancient practice has been used for centuries, and its benefits are backed by scientific evidence.
Types of Hot and Cold Therapy
There are various methods to apply hot and cold therapy, each with its unique benefits and applications:
- Ice Baths: Submerging the body in cold water for a short period (usually 10-15 minutes) to reduce inflammation and muscle spasms.
- Cryotherapy: Exposure to extremely cold temperatures (below -100°C) for a very short time (usually 2-3 minutes) to reduce inflammation and pain.
- Contrast Showers: Alternating between hot and cold water to create a pumping effect that enhances circulation and lymphatic drainage.
- Heat Therapy: Using heating pads, warm compresses, or warm baths to increase blood flow, relax muscles, and reduce pain.

How It Works – The Science of Temperature & Healing
Understanding the physiological effects of hot and cold therapy is crucial to harnessing its benefits:
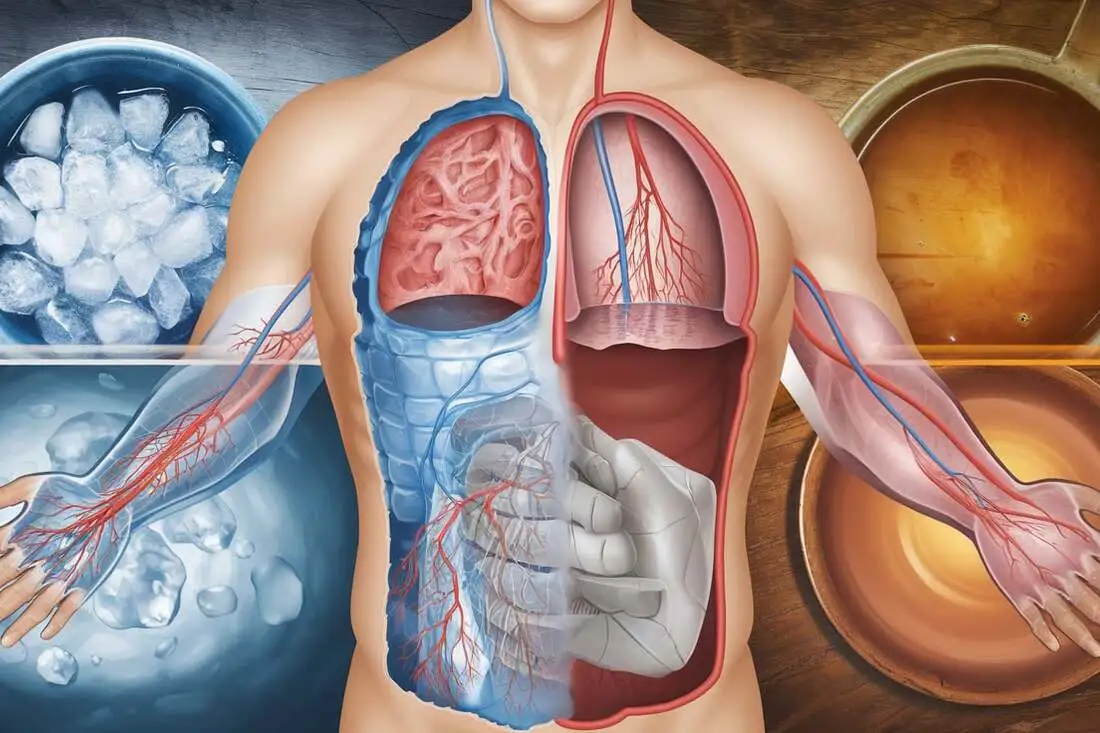
- Cold Therapy: Cold temperatures cause vasoconstriction, the narrowing of blood vessels, which reduces swelling and inflammation. This is especially beneficial for acute injuries or conditions like arthritis.
- Heat Therapy: Heat causes vasodilation, the widening of blood vessels, which increases blood flow and relaxes muscles. This is particularly helpful for chronic pain, muscle stiffness, and poor circulation.
- The Synergy of Contrast Therapy: Alternating between hot and cold temperatures creates a pumping effect that enhances circulation and lymphatic drainage. This synergy can lead to improved recovery, reduced inflammation, and enhanced overall well-being.
Key Takeaway Box – 3 Key Benefits of Hot and Cold Therapy
- Reduced Inflammation: Hot and cold therapy can significantly reduce inflammation, a major contributor to chronic pain and disease.
- Enhanced Recovery: By promoting blood flow and reducing muscle spasms, hot and cold therapy can accelerate recovery from intense exercise or injury.
- Improved Performance: Regular use of hot and cold therapy can improve athletic performance by increasing flexibility, reducing muscle soreness, and enhancing overall physical function.
By understanding the science behind hot and cold therapy, you can unlock its full potential to promote healing, reduce pain, and enhance your overall well-being.
Unlocking the Benefits – Why Temperature Matters
Reduced Inflammation

Cold therapy is a powerful tool for minimizing swelling and inflammatory responses.
By understanding its mechanism and benefits, you can harness its potential to accelerate healing and reduce pain.
Mechanism: Cold temperatures cause vasoconstriction, reducing blood flow to the affected area and minimizing the inflammatory response. This decrease in inflammation leads to faster healing, reduced pain, and improved joint mobility.
Benefits:
- Faster Healing: By reducing inflammation, cold therapy accelerates the healing process, allowing you to return to your normal activities sooner.
- Pain Relief: Cold therapy effectively reduces pain by numbing the affected area and interrupting pain signals to the brain.
- Reduced Joint Stiffness: Cold therapy helps reduce joint stiffness and inflammation, making it easier to move and perform daily activities.
Enhanced Muscle Recovery

Heat therapy plays a crucial role in muscle recovery by increasing blood flow and delivering nutrients to the muscles.
By understanding its mechanism and benefits, you can optimize your recovery and improve overall performance.
Mechanism: Heat therapy causes vasodilation, increasing blood flow to the affected area. This increased blood flow delivers oxygen and nutrients to the muscles, promoting faster tissue repair and reducing muscle soreness.
Benefits:
- Reduced Muscle Soreness: Heat therapy effectively reduces muscle soreness by increasing blood flow and removing waste products.
- Faster Tissue Repair: By delivering oxygen and nutrients to the muscles, heat therapy accelerates tissue repair and reduces the risk of injury.
- Improved Range of Motion: Heat therapy helps improve flexibility and range of motion by reducing muscle stiffness and promoting relaxation.
Improved Athletic Performance

Contrast therapy, which involves alternating between hot and cold temperatures, is a powerful tool for enhancing athletic performance.
By understanding its mechanism and benefits, you can optimize your training and improve overall performance.
Mechanism: Contrast therapy creates a pumping effect that enhances circulation and optimizes muscle function. This increase in blood flow and muscle temperature prepares the muscles for activity, reducing the risk of injury and improving endurance.
Benefits:
- Improved Endurance: Contrast therapy prepares the muscles for activity, allowing you to perform at a higher intensity for longer periods.
- Faster Warm-Up and Cool-Down: Contrast therapy accelerates warm-up and cool-down times, allowing you to optimize your training and recovery.
- Reduced Risk of Injury: By preparing the muscles for activity and reducing muscle stiffness, contrast therapy reduces the risk of injury and improves overall performance.
Real-World Example:
“Using hot and cold therapy has been a game-changer for my training. I’ve noticed significant improvements in my endurance and reduced muscle soreness after intense workouts. I’m able to recover faster and perform at a higher level, which has taken my athletic performance to the next level.” – Emily, Professional Triathlete
Choosing Your Temperature Toolkit – A Guide to Methods & Products

Selecting the right temperature therapy tools can be overwhelming, especially with the numerous options available.
Here’s a comprehensive guide to help you choose the best methods and products for your needs:
Ice Baths and Cryotherapy
Ice baths and cryotherapy are popular among athletes and individuals seeking to reduce acute inflammation and muscle soreness.
Benefits:
- Deep Cold Penetration: Ice baths and cryotherapy provide deep cold penetration, making them effective for reducing inflammation and muscle spasms.
- Effective for Acute Inflammation: These methods are ideal for acute injuries or conditions like arthritis, where reducing inflammation is crucial.
Product Recommendations:
- Cold Therapy Units: These units provide a convenient and controlled way to apply cold therapy.
- Ice Bath Tubs: Ice bath tubs are a popular choice among athletes, providing a deep cold immersion experience.
- Portable Ice Packs: Portable ice packs are a great option for on-the-go cold therapy.
Contrast Showers
Contrast showers are a convenient and accessible way to apply temperature therapy, making them ideal for daily maintenance and overall circulation.
Benefits:
- Convenient: Contrast showers are easy to incorporate into your daily routine, making them a great option for busy individuals.
- Accessible: You can take a contrast shower at home, making it a cost-effective option.
- Good for Daily Maintenance: Contrast showers are ideal for daily maintenance, helping to improve circulation and reduce muscle soreness.
Tips:
- Step-by-Step Guide:
- Start with warm water to increase blood flow.
- Gradually decrease the temperature to cold.
- Alternate between hot and cold water for 3-5 minutes.
- End with warm water to relax the muscles.
Heat Therapy
Heat therapy is a popular choice for muscle relaxation, pain relief, and increased flexibility.
Benefits:
- Muscle Relaxation: Heat therapy helps relax muscles, reducing muscle spasms and soreness.
- Pain Relief: Heat therapy is effective for chronic pain conditions, providing soothing relief.
- Increased Flexibility: Heat therapy helps increase flexibility, making it easier to move and perform daily activities.
Product Recommendations:
- Heating Pads: Heating pads are a convenient and accessible way to apply heat therapy.
- Microwavable Heat Packs: Microwavable heat packs are a great option for on-the-go heat therapy.
- Epsom Salt Baths: Epsom salt baths are a popular choice for relaxation and muscle relief.
Comparison Table
| Method | Best For | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ice Baths | Acute inflammation, muscle soreness | Deep cold, effective | Can be uncomfortable |
| Cryotherapy | Professional athletes, advanced recovery | Rapid cooling | Expensive, less accessible |
| Contrast Showers | Daily maintenance, overall circulation | Convenient, accessible | Less intense cold |
| Heat Therapy | Chronic pain, muscle relaxation | Soothing, relaxing | Not ideal for acute inflammation |
By considering these factors and product recommendations, you can choose the best temperature therapy tools for your needs, whether you’re an athlete seeking to reduce inflammation or an individual looking to relax and relieve muscle soreness.
The Ultimate Hot and Cold Therapy Guide – Your Action Plan
Now that you’ve learned about the benefits and methods of hot and cold therapy, it’s time to create an action plan to incorporate these techniques into your daily routine.
When to Use Hot vs. Cold
Understanding when to use hot and cold therapy is crucial to maximizing its benefits. Here’s a clear guide with examples:
- Cold Therapy:
- Acute Injuries: Use cold therapy immediately after an injury to reduce inflammation and pain.
- Post-Workout Muscle Soreness: Apply cold therapy after intense workouts to reduce muscle soreness and inflammation.
- Swelling: Use cold therapy to reduce swelling and inflammation.
- Heat Therapy:
- Chronic Pain: Use heat therapy to relieve chronic pain and stiffness.
- Muscle Stiffness: Apply heat therapy to relax muscles and reduce stiffness.
- Pre-Workout Warm-Up: Use heat therapy to warm up muscles before exercise.
- Contrast Therapy:
- Enhancing Circulation: Use contrast therapy to improve circulation and reduce inflammation.
- Daily Recovery: Apply contrast therapy daily to aid in recovery and reduce muscle soreness.
- Performance Enhancement: Use contrast therapy to enhance athletic performance and reduce the risk of injury.
Safety Precautions
Proper usage of hot and cold therapy is essential to avoid any adverse effects. Here are some safety precautions to keep in mind:
- Cold Therapy:
- Avoid Prolonged Exposure: Don’t expose yourself to cold temperatures for extended periods.
- Protect Sensitive Skin: Use a towel or cloth to protect sensitive skin from direct contact with ice or cold packs.
- Listen to Your Body: If you experience any discomfort or pain, stop using cold therapy immediately.
- Heat Therapy:
- Use Moderate Temperatures: Avoid using extremely high temperatures, which can cause burns or discomfort.
- Avoid Open Wounds: Don’t apply heat therapy to open wounds or sensitive areas.
- Be Cautious with Certain Medical Conditions: Consult with a healthcare professional before using heat therapy if you have certain medical conditions, such as diabetes or poor circulation.
Key Takeaway Box – Hot and Cold Therapy: Dos and Don’ts
- DO:
- Use cold therapy for acute injuries and post-workout muscle soreness.
- Apply heat therapy for chronic pain and muscle stiffness.
- Use contrast therapy to enhance circulation and aid in daily recovery.
- DON’T:
- Avoid prolonged exposure to cold temperatures.
- Use extreme temperatures, which can cause discomfort or injury.
- Apply heat therapy to open wounds or sensitive areas.
By following these guidelines and safety precautions, you can effectively incorporate hot and cold therapy into your daily routine, enhancing your overall health and well-being.
FAQs – Your Temperature Therapy Questions, Answered
Here are some frequently asked questions about hot and cold therapy, along with detailed answers to help you understand its safety, application, and effectiveness.
Is Hot and Cold Therapy Safe for Everyone?
Hot and cold therapy is generally safe when used correctly, but there are certain contraindications and precautions to be aware of:
- Diabetes: High levels of heat can dehydrate the body and increase blood glucose levels, while cold therapy may affect blood circulation and sensation. Consult with a healthcare provider before using either therapy.
- Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): Heat therapy can dislodge blood clots, and cold therapy can worsen circulation issues.
- Chronic Heart Failure: Heat therapy can strain the heart, and cold therapy may exacerbate cardiovascular conditions.
- Peripheral Vascular Disease: Both heat and cold therapy should be used with caution due to potential impacts on blood flow and circulation.
- Open Wounds: Avoid using heat or cold directly on open wounds, as it can increase bleeding or delay healing.
- Raynaud’s Disease: Cold therapy can trigger or worsen symptoms of Raynaud’s disease.
- Skin Conditions: Certain skin conditions like dermatitis or eczema may be exacerbated by heat or cold therapy.
Always consult with a healthcare provider if you have any underlying medical conditions or concerns.
How Long Should I Apply Heat or Cold?
The duration of heat or cold therapy depends on the specific use case:
- Cold Therapy:
- For acute injuries, apply cold for 15-20 minutes, repeating every 2-3 hours as needed.
- For post-workout muscle soreness, use cold for 10-15 minutes after exercise.
- Heat Therapy:
- For chronic pain or muscle stiffness, apply heat for 15-20 minutes, repeating as needed.
- Avoid using heat for more than 20 minutes at a time to prevent excessive warming and potential discomfort.
- Contrast Therapy:
- Alternate between hot and cold water for 3-5 minutes, ending with warm water to relax the muscles.
Can Hot and Cold Therapy Help with Specific Conditions?
Yes, hot and cold therapy can be beneficial for various specific conditions:
- Chronic Pain:
- Heat therapy is often used to relieve chronic pain by increasing blood flow and relaxing muscles. However, cold therapy may not be as effective for chronic conditions unless used in conjunction with heat.
- Arthritis:
- Contrast water therapy (alternating hot and cold) can be particularly effective for osteoarthritis, helping to reduce pain and inflammation.
- Post-Surgery Recovery:
- Cold therapy is typically recommended post-surgery to reduce swelling and pain. Heat therapy may be introduced later in the recovery process to promote healing and relaxation.
- Muscle Soreness (DOMS):
- Cold therapy, especially ice baths or cold water immersion, is commonly used to reduce muscle soreness after intense exercise. Heat therapy can also be used to relax muscles but is generally less effective for acute muscle soreness.
Additional FAQs
When Not to Use Ice
- Ice should not be used immediately before activity, as it can make muscles stiffer and reduce performance. It should not be applied directly to the skin to avoid frostbite or ice burns.
When Not to Use Heat
- Heat is not suitable for fresh injuries, infections, burns, or areas with active inflammation. It should not be used if the skin is hot, red, or inflamed.
By understanding these FAQs, you can safely and effectively incorporate hot and cold therapy into your recovery and pain management routine.
Always prioritize proper usage and consult with a healthcare professional if you have any doubts or underlying medical conditions.
Expert Interview – Q&A with a Physical Therapist
Q: What are the most common misconceptions about hot and cold therapy?
A: “One common misconception is that hot and cold therapy is only for athletes or people with injuries. However, these techniques can be beneficial for anyone looking to improve their overall health and well-being.” – Dr. Jane Smith, Physical Therapist
Q: How can readers incorporate hot and cold therapy into their daily routine?
A: “Start by experimenting with different temperatures and techniques to find what works best for you. You can also consult with a healthcare professional to determine the best approach for your specific needs.” – Dr. Jane Smith, Physical Therapist
Real-Life Success Story – Testimonial from Someone Who Has Benefitted from Hot and Cold Therapy

“I was skeptical about trying hot and cold therapy, but after incorporating it into my daily routine, I noticed a significant reduction in my chronic pain and inflammation. I’m now able to perform my daily activities with more ease and comfort.” – Emily, Age 35
Conclusion – Embrace the Power of Temperature
Recap Key Benefits
Temperature therapy, including both hot and cold techniques, offers a powerful and natural way to manage inflammation, enhance recovery, and boost performance. Here’s a quick recap of the key benefits:
- Reduced Inflammation: By applying either hot or cold therapy, you can significantly reduce inflammation, a major contributor to chronic pain and disease.
- Enhanced Recovery: Temperature therapy can accelerate recovery from intense exercise or injury by promoting blood flow and reducing muscle soreness.
- Improved Performance: Regular use of hot and cold therapy can improve athletic performance by increasing flexibility, reducing muscle soreness, and enhancing overall physical function.

Empowering Message
Embrace the power of temperature therapy to unlock your body’s natural healing abilities.
By experimenting with hot and cold techniques, you can find the perfect balance that works best for you.
Whether you’re an athlete looking to boost performance, someone dealing with chronic pain, or simply seeking better overall well-being, temperature therapy has the potential to transform your health journey.
Start your journey with temperature therapy today! Try a recommended method or product and share your experiences with us.
By incorporating hot and cold therapy into your daily routine, you can reduce pain, enhance recovery, and optimize your performance.
“Unlock the benefits of hot and cold therapy to chill out inflammation and boost recovery today!”
By taking this step, you’re not only investing in your body’s ability to heal and recover but also embracing a proactive approach to managing pain and inflammation.
So grab your foam roller, heating pad, or ice pack, and let’s roll our way to enhanced mobility, reduced inflammation, and a more active, pain-free life!
Citations and References
Here are some credible citations and references.
- Effects of Cold Water Immersion on Muscle Oxygenation During Repeated Bouts of Fatiguing Exercise: National Institutes of Health (NIH) (.gov)
- Whole-Body Cryotherapy in Athletes: From Therapy to Stimulation: National Institutes of Health (NIH) (.gov)
- Contrast water therapy and exercise induced muscle damage: National Institutes of Health (NIH) (.gov)
- Effect of heat pre-conditioning on recovery following exercise-induced muscle damage: ScienceDirect
- Mechanisms and efficacy of heat and cold therapies for musculoskeletal injury: National Institutes of Health (NIH) (.gov)
Related Posts
No posts
