Struggling to catch your breath?
Feeling increasingly short of breath during daily activities?
These could be signs of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD), a group of progressive lung diseases that make breathing difficult.
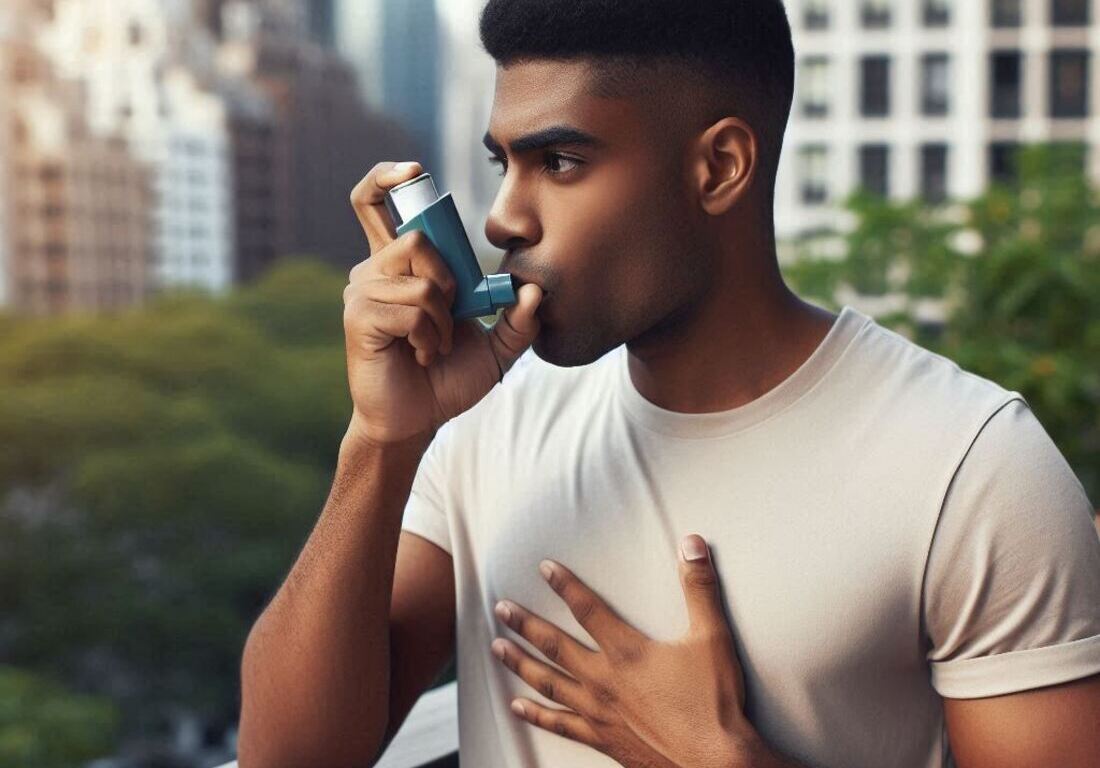

This blog delves into the world of COPD, providing you with essential information about the condition.
We’ll explore the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for COPD, empowering you to take charge of your lung health.
Understanding COPD
COPD is an umbrella term for progressive lung diseases, primarily emphysema and chronic bronchitis.
These conditions damage the lungs, causing airways to become narrowed and blocked, hindering airflow.
This makes breathing increasingly difficult and can significantly impact your daily life.
Causes of COPD
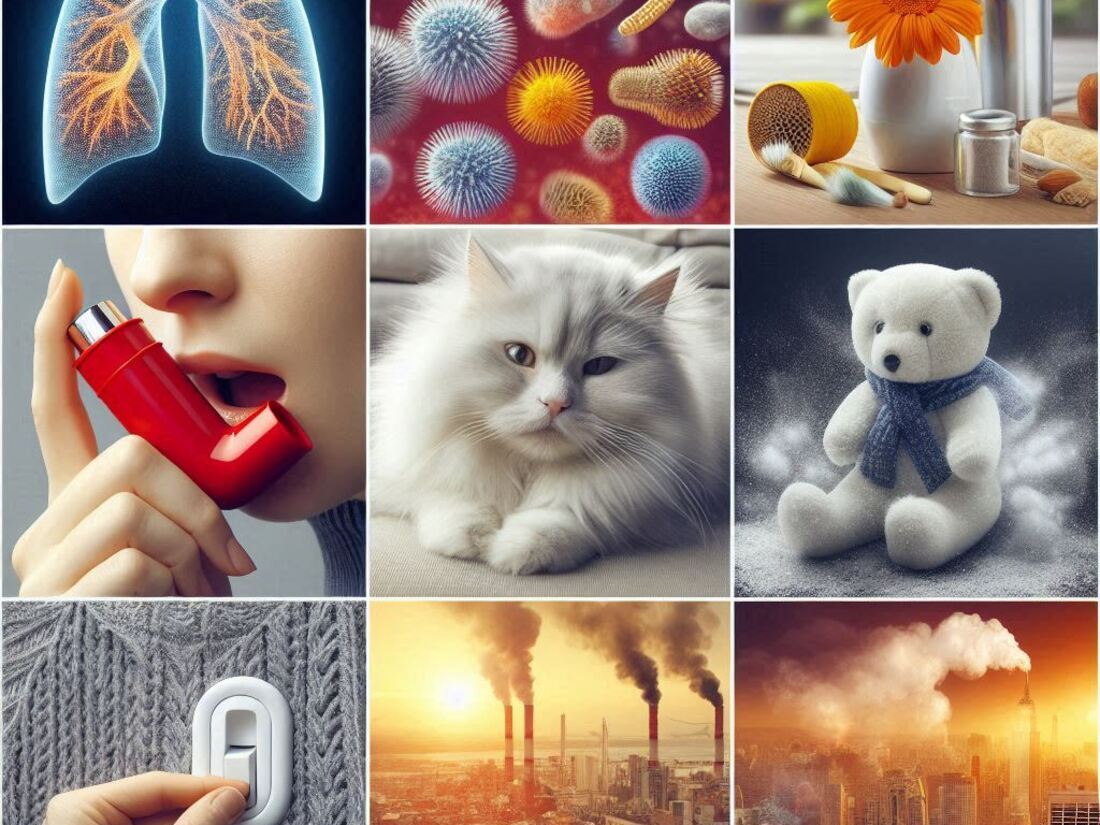

The leading cause of COPD is smoking, including cigarettes, cigars, and pipes.
Long-term exposure to secondhand smoke and air pollution can also contribute to the development of COPD.
Symptoms of COPD

Early symptoms of COPD can be subtle, often mistaken for normal signs of aging.
As the disease progresses, symptoms become more prominent and may include:
- Shortness of breath, especially during physical activity
- Chronic cough, which may produce mucus (phlegm)
- Chest tightness
- Wheezing, a whistling sound during breathing
- Frequent respiratory infections
- Fatigue and low energy levels
- Unintentional weight loss in later stages
If you experience any of these symptoms, especially if they are persistent or worsen over time, consult your doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment planning.
Diagnosis of COPD
COPD is typically diagnosed through a combination of tests, including:
- Medical history: Your doctor will discuss your symptoms, risk factors, and smoking history.
- Physical examination: This may involve listening to your lungs for abnormal sounds.
- Spirometry: This lung function test measures how much air you can forcefully exhale and how quickly.
- Chest X-ray: This imaging test can reveal abnormalities in your lungs, although it cannot definitively diagnose COPD.
Treatment Options for COPD
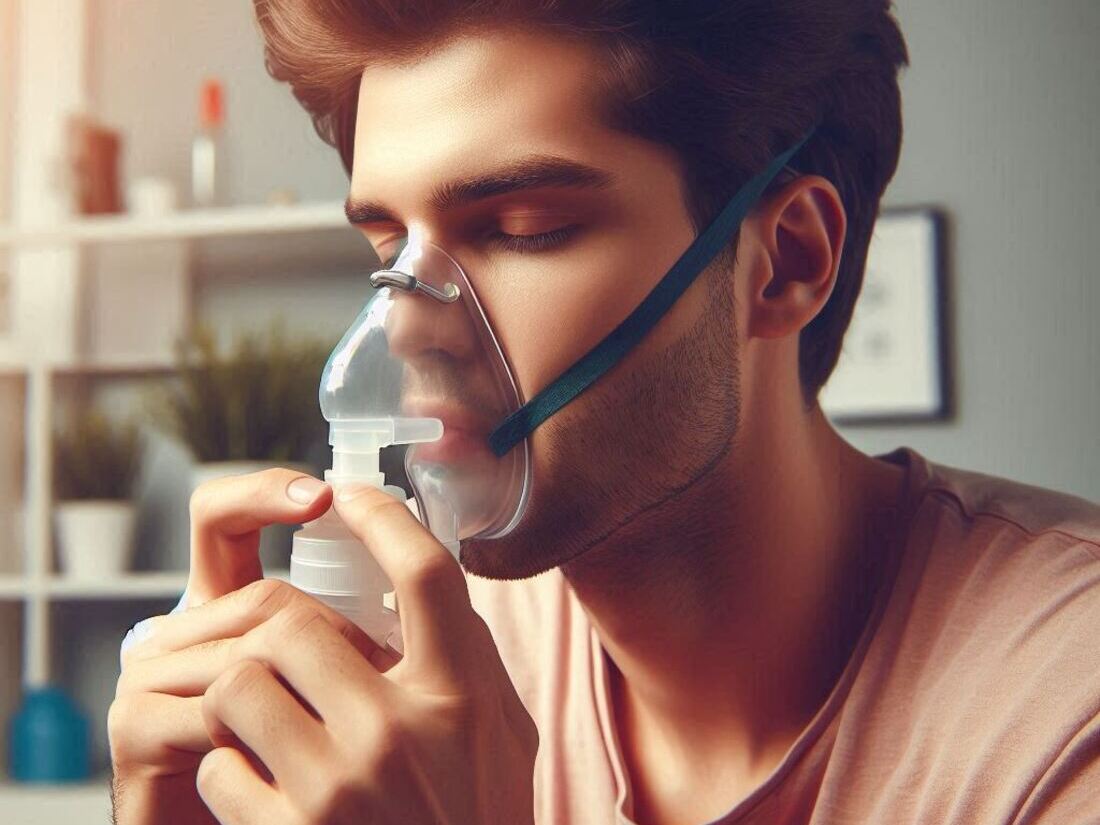

While there is no cure for COPD, there are treatments available to manage symptoms, slow disease progression, and improve your quality of life.
These include:
- Smoking cessation: Quitting smoking is the single most important step you can take to manage COPD and prevent further lung damage.
- Medications: Bronchodilators relax the airways to improve airflow. Inhaled corticosteroids can reduce inflammation in the airways.
- Pulmonary rehabilitation: These exercise programs help improve your strength, stamina, and ability to breathe.
- Oxygen therapy: In severe cases, supplemental oxygen may be needed to increase blood oxygen levels.
Living with COPD
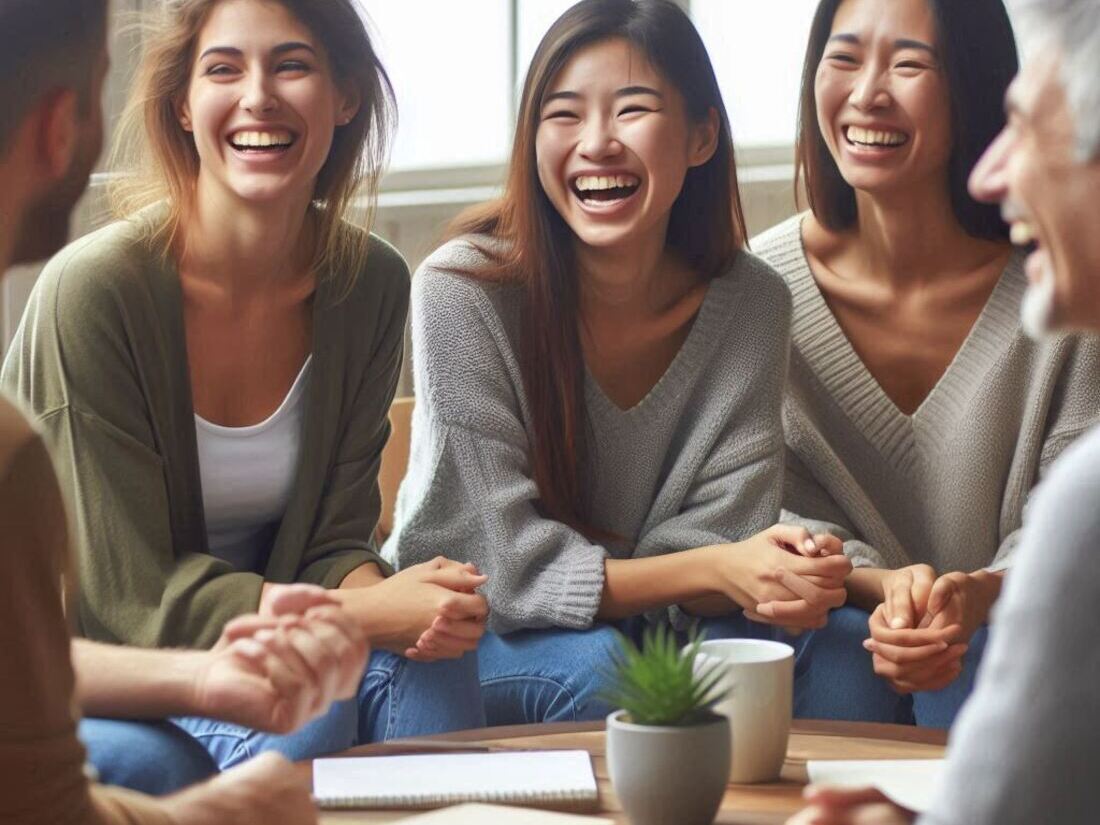

Although COPD is a chronic condition, with proper management and lifestyle changes, you can live a full and active life.
Here are some tips:
- Get Vaccinated: Regularly get your flu shot and pneumonia vaccine to help prevent respiratory infections that can worsen COPD symptoms.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Being overweight can place additional strain on your lungs.
- Eat a Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains provides your body with the nutrients it needs for optimal health.
- Manage Stress: Stress can worsen breathing difficulties. Practice relaxation techniques like yoga or meditation.
- Join a Support Group: Connecting with others who understand your challenges can be a source of encouragement and information.
Conclusion
COPD is a serious lung condition, but it is manageable.
By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, you can take control of your COPD and breathe easier.
Remember, early diagnosis and treatment are essential for optimal lung health.
Don’t hesitate to consult your doctor if you experience any concerning symptoms.
Here are some resources for further information:
- National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute: https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/copd
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: https://www.cdc.gov/copd/index.html
Disclaimer: The information in this blog is for educational purposes only and should not be construed as medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare professional for diagnosis and treatment of COPD.
