Have you ever crushed a workout, but your mind won’t stop racing?
You’re not alone.
While that post-workout glow is amazing, it’s common to feel wired, anxious, or stressed afterward.
It’s more common than you might think.
Exercise, while fantastic, can sometimes trigger stress due to cortisol release, pressure to perform, or overtraining.
You might end up feeling more frazzled than zen.
But don’t worry, there’s a simple and natural solution – Breathing for Stress and Anxiety Relief.

Believe it or not, mastering a few key breathing techniques can quickly melt away that post-workout tension, calm your racing mind, and leave you feeling truly refreshed and centered.
In this guide, you’ll discover easy-to-learn breathing exercises to take control of your stress and transform your post-workout experience into a peaceful and rejuvenating one.
You’ll also learn the science-backed ways breathing benefits you.
Key Takeaway:
Breathing techniques are a fast, effective way to combat post-workout stress.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this blog post is for educational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional before making any changes to your health or treatment plan.
The Science Behind Breathing for Stress Relief
Okay, so breathing techniques sound calming, but what’s really going on inside your body when you practice them?
It’s not just ‘in with the good air, out with the bad.’
There’s a fascinating interplay of physiological processes at work.
Parasympathetic Nervous System (PNS) Activation – Your Body’s Natural Chill Pill
Think of your nervous system as having two main branches: the sympathetic (fight-or-flight) and the parasympathetic (rest-and-digest).
When you’re stressed, your sympathetic nervous system is in overdrive.
Deep, slow breathing flips the switch, activating your PNS and signaling to your body that it’s safe to relax.
(Citation: Study on breathing and PNS activation)
Heart Rate Variability (HRV): Building Stress Resilience
Heart Rate Variability (HRV) measures the variation in time intervals between your heartbeats.
A higher HRV indicates that your nervous system is more adaptable and resilient to stress.
Deep breathing has been shown to improve HRV, making you better equipped to handle life’s challenges.
(Citation: Study on breathing and HRV)
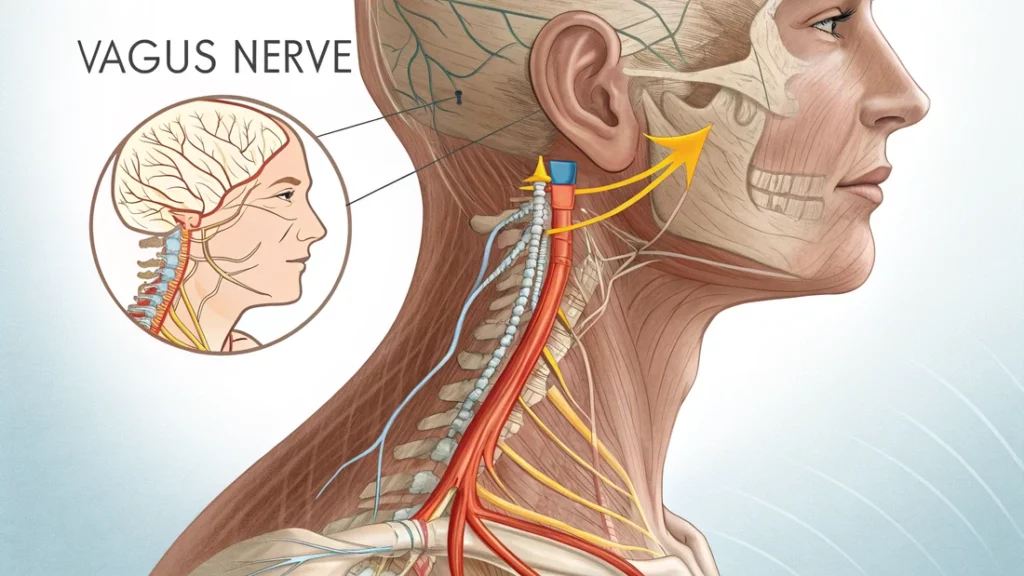
Vagus Nerve Stimulation: The Mind-Body Superhighway
The vagus nerve is a major cranial nerve that connects your brain to many organs, including your heart, lungs, and gut.
It plays a key role in regulating the parasympathetic nervous system.
Deep breathing stimulates the vagus nerve, which helps to reduce stress, lower heart rate, and promote relaxation.
(Citation: Study on breathing and vagus nerve stimulation)
Cortisol Reduction: Taming the Stress Hormone
Cortisol, the stress hormone, is released during times of stress and can have negative effects on your body and mind.
Chronic stress can lead to elevated cortisol levels, which can contribute to anxiety, sleep problems, and other health issues.
Deep breathing has been shown to lower cortisol levels, helping you manage stress and promote overall well-being.
(Citation: Study on breathing and cortisol levels)
This is the basic understanding on why people recommend breathing.
5 Powerful Breathing Techniques for Post-Workout Stress Relief
Ready to take control of your post-workout stress?
Here are 5 powerful breathing techniques you can use to calm your mind and find your center:
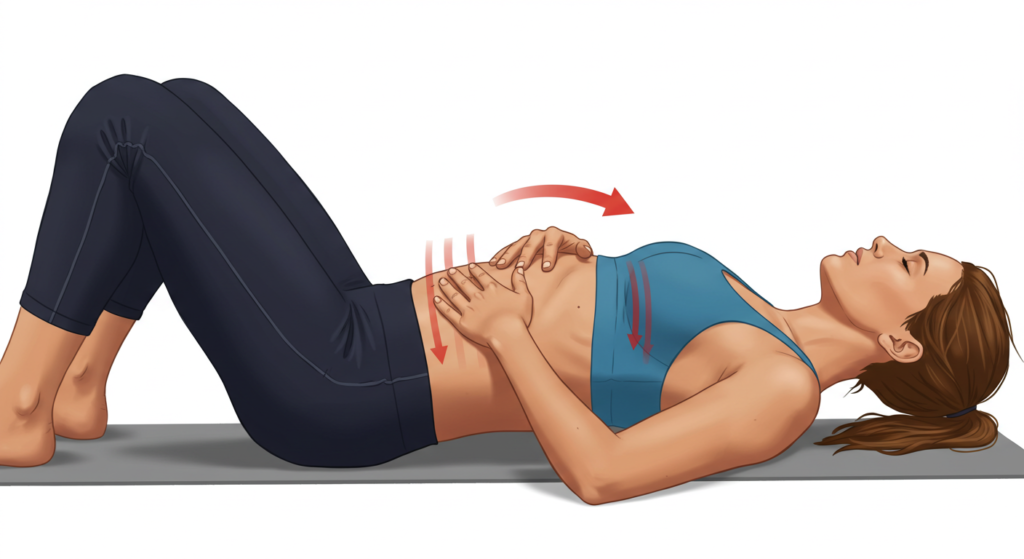
- Diaphragmatic Breathing (Belly Breathing)
- Benefits: Reduces anxiety, promotes relaxation, lowers heart rate.
- Instructions:
- Lie on your back with knees bent, or sit comfortably.
- Place one hand on your chest, the other on your belly.
- Inhale slowly through your nose, expanding your belly.
- Exhale slowly through your mouth, allowing your belly to fall.
- Repeat for 5-10 minutes, focusing on slow, deep breaths.
- Timing: Immediately after workout, before bed, or anytime you feel stressed.
- Variations: Seated, lying down, with guided meditation.
- Box Breathing
- Benefits: Calms the nervous system, improves focus, and reduces stress.
- Instructions:
- Sit comfortably with your back straight.
- Exhale completely.
- Inhale slowly through your nose for a count of 4.
- Hold your breath for a count of 4.
- Exhale slowly through your mouth for a count of 4.
- Hold your breath again for a count of 4.
- Repeat for 5-10 minutes.
- Timing: Anytime after workout, especially if you’re feeling anxious.
- Variations: Adjust the count (e.g., 5-5-5-5), visualize a calming image.
- Alternate Nostril Breathing
- Benefits: Balances the nervous system, reduces anxiety, and promotes relaxation.
- Instructions:
- Sit comfortably with your back straight.
- Close your right nostril with your right thumb.
- Inhale deeply through your left nostril.
- Release your right nostril and close your left nostril with your ring finger.
- Exhale slowly through your right nostril.
- Inhale through your right nostril.
- Release your left nostril and close your right nostril with your right thumb.
- Exhale slowly through your left nostril.
- Repeat for 5-10 minutes.
- Timing: When you need to calm down, especially before or after a workout.
- Variations: Adjust the duration of the breaths.
- Progressive Muscle Relaxation (PMR) with Breathing
- Benefits: Reduces muscle tension, promotes relaxation, and lowers anxiety.
- Instructions: (Integrate diaphragmatic breathing with each step)
- Find a comfortable position.
- Take a deep breath. As you inhale, tense a specific muscle group (e.g., your right fist) for 5-10 seconds.
- As you exhale, slowly release the tension in the muscle.
- Repeat with each muscle group (e.g., face, shoulders, arms, legs).
- Focus on the feeling of relaxation as you release each muscle.
- Timing: Before bed for better sleep.
- Variations: Full body PMR, focused on specific areas.
- Lion’s Breath (Simhasana)
- Benefits: Releases tension in the face and jaw, calms the mind, and promotes emotional release.
- Instructions:
- Kneel comfortably with your hands on your knees or thighs.
- Inhale deeply through your nose.
- Open your mouth wide, stick out your tongue, and exhale forcefully, making a “ha” sound.
- Imagine you are roaring like a lion.
- Repeat several times.
- Timing: As needed, when you want to relieve tension in jaw.
Table – Comparing Breathing Techniques for Post-Workout Stress Relief
| Technique | Primary Benefits | Timing | Difficulty | Key Cue |
| Diaphragmatic Breathing | Reduces anxiety, promotes relaxation | Immediately after workout, before bed, anytime you feel stressed | Easy | Focus on expanding your belly with each inhale. |
| Box Breathing | Calms the nervous system, improves focus | Anytime after workout, especially if you’re feeling anxious | Medium | Inhale-Hold-Exhale-Hold for equal counts. |
| Alternate Nostril Breathing | Balances the nervous system, reduces anxiety | When you need to calm down, especially before or after a workout | Medium | Close one nostril at a time and alternate your breathing. |
| PMR with Breathing | Reduces muscle tension, promotes relaxation | Before bed for better sleep. | Medium | Tense and release muscle groups while breathing deeply. |
| Lion’s Breath | Releases tension in the face and jaw | As needed, when you want to relieve tension in the face and jaw | Easy | Open your mouth wide, stick out your tongue, and exhale forcefully. Imagine roaring like a lion! |
This table provides a quick reference guide for readers to choose the technique that best suits their needs and preferences.
Building Your Breathing Schedule
Here are a few times in which breathing is most helpful:
- Immediately Post Workout: For blood/oxygen.
- Throughout the day: During moments of stress.
- Before Bed: To prepare for rest.
Even breathing can be difficult, so here are some common problems:
- Difficulty Focusing: Try meditation.
- Feeling Restless: Switch techniques and practice breathing while walking.
- Hyperventilating: Stop immediately!
Disclaimer: If you experience any discomfort, dizziness, or other adverse symptoms while practicing these techniques, stop immediately and seek medical advice. The author and publisher of this blog post are not responsible for any adverse effects or complications that may arise from the use of the information provided herein.
Creating a Post-Workout Breathing Routine
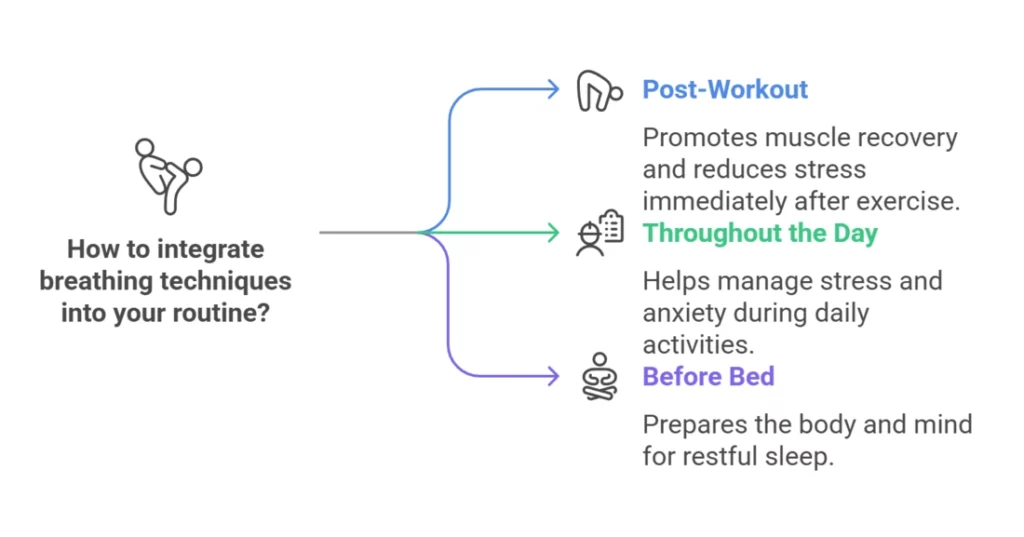
Now you know a bunch of techniques to choose from, but how do you integrate them all?
Here is what is recommended:
- When to Practice:
- Immediately After Your Workout: Dedicate 5-10 minutes to deep breathing to promote muscle recovery and reduce post-exercise stress.
- Throughout the Day: Take short breathing breaks during your workday or anytime you feel stressed or anxious.
- Before Bed: Practice deep breathing for 10-15 minutes to calm your mind and prepare your body for sleep.
- How Often to Practice:
- Aim for at least one dedicated deep breathing session per day.
- Incorporate short breathing breaks throughout the day.
- The more consistent you are, the more benefits you’ll experience.
- Creating a Calming Environment:
- Find a quiet space where you won’t be disturbed.
- Dim the lights or use natural lighting.
- Play calming music or nature sounds.
- Use aromatherapy (e.g., lavender, chamomile).
- Sample Post-Workout Breathing Schedule
- After Cooldown : Diaphragmatic Breathing for 5 mins.
- During Lunch : Box Breathing for 5 mins
- At Bed: 4-7-8 Breathing for 5 mins.
The more consistent you do, the better.
Combining Breathing with other Strategies
Breathing is good, but combining it with other things makes it even better.
- Mindfulness Meditation:
- Pair meditation with breathing as you sit and focus on your breath.
- Yoga and Stretching
- Practice yoga and stretching with specific breathing like Lion’s Breath to improve calmness.
- Progressive Muscle Relaxation
- As we tense our muscles, incorporate breathing as that moment might induce anxiety.
The more techniques, the better your well-being.
Common Problems and How to Solve Them
Even simple exercises can be difficult, these troubleshooting helps answer some potential problems.
- Difficulty Focusing:
- Problem: Thoughts always take you to another world.
- Solution: Start with short sessions (e.g., 5 minutes) and gradually increase the duration as your focus improves. Try guided meditations.
- Feeling Restless:
- Problem: You find it hard to sit still and relax.
- Solution: Try dynamic breathing exercises (e.g., Lion’s Breath) or practice breathing while walking or doing a gentle activity like yoga.
- Hyperventilation:
- Problem: If you may experience over breathing, you should contact a healthcare professional.
- Solution: This requires professional help.
Resources and Tools
To further assist you we have found some resources that are easy to start with.
- Apps
- Books
- Wherever You Go, There You Are -This book is about reducing stress and finding quiet reflective moments to bring into your life. This classic, bestselling guide is updated, and this will help you find the calmness you are chasing!
- Declutter Your Mind– Feeling overwhelmed by racing thoughts and constant distractions? This book provides practical techniques to regain focus, manage anxiety, and create a calmer, more intentional life. Learn how to silence the mental chatter and reclaim your inner peace.
Note: As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases at no cost to you.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Here are some common questions about Breathing Techniques and Stress relief.
- Q: How long does it take to see results?
- A: Consistency is key and effects vary. Try a few weeks.
- Q: Is it normal to feel some discomfort when breathing?
- A: It is but if it becomes a problem do seek a medical professional.
- Q: What if I can’t fit all the techniques into my plan?
- A: Focus on one or two techniques or what is in line with your lifestyle.
- Q: Can breathing exercises completely eliminate stress and anxiety?
- A: It can’t, professional help might be needed.
- Q: What time of the day should I do the breathing exercise?
- A: It varies with you, start with pre or post workout, or before bed, or even a combination.
- Q: How long can I do the breathing exercise for?
- A: Start slow and increase as you go.
Conclusion – Take Control of Your Mind and Body
Breathing techniques can be beneficial by improving one’s recovery, and relieving post-workout stress.
This simple and natural technique is your personal weapon.
You have been given a tool to further improve your well-being and it is best that you follow this knowledge to be your best!
Remember, it is easy to be overcome by post-workout stress, which is where the importance of today’s learning is the most useful to you!
This is your opportunity to say you won and do a victory roar!
Download a Free Guide to start today!



