We all take a deep breath for granted, but the air we inhale can often be laden with harmful pollutants, jeopardizing our lung health.
Air pollution is a growing concern, linked to a variety of respiratory problems and posing a significant threat to our well-being.

Here we will delve into the impact of air pollution on lung health.
We’ll explore the types of pollutants, their health effects, and how you can take steps to protect yourself from the harmful effects of air pollution.
Understanding the Invisible Threat: Types of Air Pollutants

While air pollution may seem invisible, it’s a complex mixture of harmful particles and gases suspended in the air.
These pollutants can vary in size and chemical composition, each posing a distinct threat to lung health.
Here are some of the most common air pollutants and their health effects:
- Particulate Matter (PM): PM refers to tiny particles that lodge deep within the lungs, causing inflammation and respiratory problems. PM2.5, fine particles less than 2.5 micrometers in diameter, are particularly harmful. Exposure to PM is linked to an increased risk of lung cancer, according to the World Health Organization (WHO) WHO PM2.5 Report 2022.
- Ground-Level Ozone: This gas, formed by chemical reactions in the atmosphere involving sunlight and pollutants, irritates the airways and can worsen asthma symptoms. The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) cites ozone as a major trigger for asthma attacks US EPA – Ground-Level Ozone Basics.
- Nitrogen Oxides (NOx): Traffic emissions are a major source of NOx, which contribute to smog formation and irritate the respiratory system. Studies have shown a link between NOx exposure and increased emergency room visits for respiratory problems American Lung Association – Health Effects of Air Pollution.
- Sulfur Dioxide (SO2): Primarily emitted from power plants, SO2 can cause coughing, wheezing, and worsen asthma attacks. The American Thoracic Society highlights the negative impacts of SO2 on lung function, particularly in children American Thoracic Society – Sulfur Dioxide.
By understanding the types of air pollutants and their sources, you can be more aware of the risks and take targeted steps to minimize exposure.
The Impact of Air Pollution on Lung Health: Beyond Just Breathing Difficulties
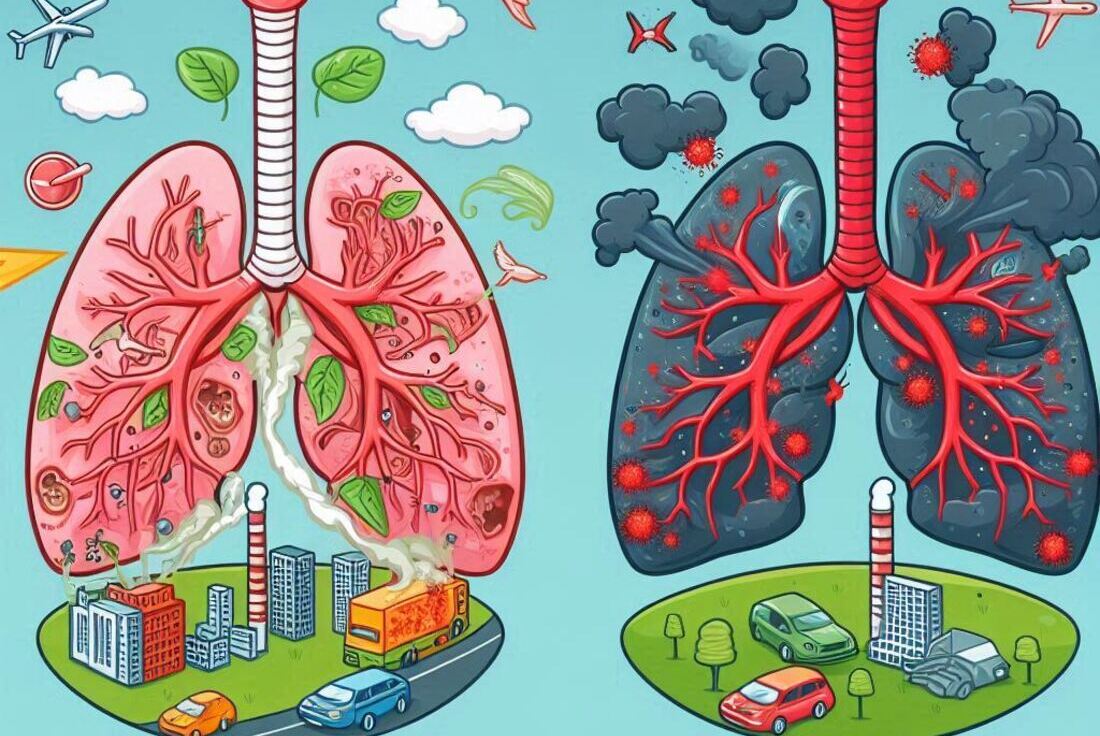
Air pollution can have a detrimental impact on lung health, causing a variety of respiratory problems.
Here’s how:
- Inflammation: Pollutants irritate and inflame the airways, leading to coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath.
- Reduced Lung Function: Air pollution can damage lung tissue and reduce lung function, making it harder to breathe.
- Exacerbation of Chronic Conditions: For people with asthma, COPD, or other chronic lung conditions, air pollution can worsen symptoms and trigger attacks.
- Increased Risk of Respiratory Infections: Air pollution can weaken the immune system, making you more susceptible to respiratory infections.
- Lung Cancer: Long-term exposure to air pollution is a risk factor for lung cancer.
The Wider Health Impacts of Air Pollution: It’s Not Just About Your Lungs
The detrimental effects of air pollution extend beyond the lungs.
Research suggests a link between long-term exposure to air pollution and an increased risk of various health problems, including:
- Heart Disease: Air pollution can damage blood vessels and contribute to heart disease, a leading cause of death globally American Heart Association – Air Pollution and Heart Disease
- Stroke: Inhaled pollutants can increase inflammation and blood clotting, raising the risk of stroke Stroke Association – Air Pollution and Stroke.
- Cancer: Long-term exposure to air pollution is a risk factor for lung cancer, as well as some other cancers National Cancer Institute – Outdoor Air Pollution and Cancer.
- Cognitive Decline: Studies suggest a link between air pollution and cognitive decline, including dementia and Alzheimer’s disease [Environmental Health Perspectives – Association of Long-Term Exposure to Air Pollution With Cognitive Decline in Older Men]
Protecting Yourself from Air Pollution: Breathe Easy and Take Action

While we can’t control air quality entirely, there are steps you can take to minimize your exposure to air pollution and protect your lungs:
- Track Air Quality Reports: Stay informed about air quality levels in your area. Many air quality monitoring websites and apps provide real-time updates. Check the Air Quality Index (AQI) from the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) US EPA – Air Quality Index (AQI).
- Limit Outdoor Activity During Peak Pollution Times: Air pollution levels often peak during rush hour or on hot, stagnant days. Reduce outdoor activity when the AQI is unhealthy or hazardous.
- Invest in Air Purifiers: Consider using air purifiers in your home and workplace to remove pollutants from the air you breathe. Look for purifiers with HEPA (High Efficiency Particulate Air) filters, which are effective at capturing PM2.5 and other airborne particles.
- Reduce Your Carbon Footprint: Choose eco-friendly transportation options like cycling, walking, or public transport. Reduce your reliance on personal vehicles to help combat air pollution at its source. Consider carpooling or using electric vehicles when possible.
- Advocate for Clean Air Policies: Contact your local representatives and urge them to enact stricter regulations on industrial emissions and support policies promoting cleaner energy sources. Renewable energy sources like solar and wind power are crucial for reducing air pollution in the long term.
Empowering Action: Advocacy for Change

While individual actions are crucial, tackling air pollution requires a collective effort.
Here’s how you can advocate for change:
- Support Clean Air Policies: Contact your local representatives and urge them to enact stricter regulations on industrial emissions and support policies promoting cleaner energy sources.
- Raise Awareness: Spread awareness about the dangers of air pollution and encourage others to take action. Share informative articles and resources on social media or discuss the issue with friends and family.
- Support Environmental Organizations: Donate to or volunteer your time with organizations working to combat air pollution and promote clean air initiatives. Look for organizations focused on clean air advocacy in your area.
By advocating for change and working together, we can create a healthier future with cleaner air for everyone.
Conclusion
Air pollution is a significant threat to lung health and overall well-being.
By understanding the risks and taking steps to protect yourself, you can minimize your exposure and safeguard your respiratory health.
Remember, even small changes can make a big difference. Let’s work together to breathe cleaner air and create a healthier future for ourselves and generations to come.



